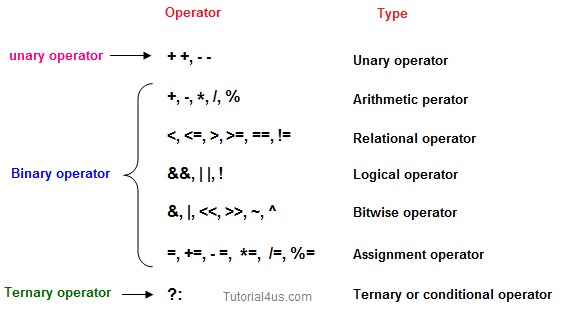
Operator is a special symbol that tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical Operation.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Ternary or Conditional Operators
Arithmetic Operators
Given table shows all the Arithmetic operator supported by C Language. Lets suppose variable Ahold 8 and B hold 3.
| Operator | Example (int A=8, B=3) | Result |
|---|---|---|
| + | A+B | 11 |
| - | A-B | 5 |
| * | A*B | 24 |
| / | A/B | 2 |
| % | A%4 | 0 |
Relational Operators
Which can be used to check the Condition, it always return true or false. Lets suppose variable Ahold 8 and B hold 3.
| Operators | Example (int A=8, B=3) | Result |
|---|---|---|
| < | A<B | False |
| <= | A<=10 | True |
| > | A>B | True |
| >= | A<=B | False |
| == | A== B | False |
| != | A!=(-4) | True |
Logical Operator
Which can be used to combine more than one Condition?. Suppose you want to combined two conditions A<B and B>C, then you need to use Logical Operator like (A<B) && (B>C). Here &&is Logical Operator.
| Operator | Example (int A=8, B=3, C=-10) | Result |
|---|---|---|
| && | (A<B) && (B>C) | False |
| || | (B!=-C) || (A==B) | True |
| ! | !(B<=-A) | True |
Truth table of Logical Operator
| C1 | C2 | C1 && C2 | C1 || C2 | !C1 | !C2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | T | T | T | F | F |
| T | F | F | T | F | T |
| F | T | F | T | T | F |
| F | F | F | F | T | T |
Assignment operators
Which can be used to assign a value to a variable. Lets suppose variable A hold 8 and B hold 3.
| Operator | Example (int A=8, B=3) | Result |
|---|---|---|
| += | A+=B or A=A+B | 11 |
| -= | A-=3 or A=A+3 | 5 |
| *= | A*=7 or A=A*7 | 56 |
| /= | A/=B or A=A/B | 2 |
| %= | A%=5 or A=A%5 | 3 |
| =a=b | Value of b will be assigned to a |
Increment and Decrement Operator in C
Increment Operators are used to increased the value of the variable by one and Decrement Operators are used to decrease the value of the variable by one in C programs.
Both increment and decrement operator are used on a single operand or variable, so it is called as a unary operator. Unary operators are having higher priority than the other operators it means unary operators are executed before other operators.
Syntax
++ // increment operator -- // decrement operator
Note: Increment and decrement operators are can not apply on constant.
Example
x= 4++; // gives error, because 4 is constant
Type of Increment Operator
- pre-increment
- post-increment
pre-increment (++ variable)
In pre-increment first increment the value of variable and then used inside the expression (initialize into another variable).
Syntax
++ variable;
Example pre-increment
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int x,i; i=10; x=++i; printf("x: %d",x); printf("i: %d",i); getch(); }
Output
x: 11 i: 11
In above program first increase the value of i and then used value of i into expression.
post-increment (variable ++)
In post-increment first value of variable is used in the expression (initialize into another variable) and then increment the value of variable.
Syntax
variable ++;
Example post-increment
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int x,i; i=10; x=i++; printf("x: %d",x); printf("i: %d",i); getch(); }
Output
x: 10 i: 11
In above program first used the value of i into expression then increase value of i by 1.
Type of Decrement Operator
- pre-decrement
- post-decrement
Pre-decrement (-- variable)
In pre-decrement first decrement the value of variable and then used inside the expression (initialize into another variable).
Syntax
-- variable;
Example pre-decrement
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int x,i; i=10; x=--i; printf("x: %d",x); printf("i: %d",i); getch(); }
Output
x: 9 i: 9
In above program first decrease the value of i and then value of i used in expression.
post-decrement (variable --)
In Post-decrement first value of variable is used in the expression (initialize into another variable) and then decrement the value of variable.
Syntax
variable --;
Example post-decrement
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int x,i; i=10; x=i--; printf("x: %d",x); printf("i: %d",i); getch(); }
Output
x: 10 i: 9
In above program first used the value of x in expression then decrease value of i by 1.
Example of increment and decrement operator
Example
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int x,a,b,c; a = 2; b = 4; c = 5; x = a-- + b++ - ++c; printf("x: %d",x); getch(); }
Output
x: 0

No comments:
Post a Comment