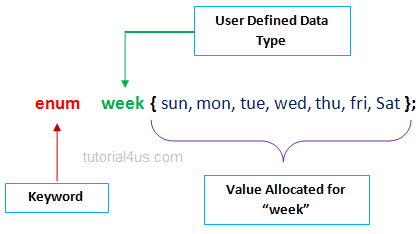
Structure is a user defined data type which hold or store heterogeneous data item or element in a singe variable. It is a Combination of primitive and derived data type.
Why Use Structure in C
In C language array is also a user defined data type but array hold or store only similar type of data, If we want to store different-different type of data in then we need to defined separate variable for each type of data.
Example: Suppose we want to store Student record, then we need to store....
- Student Name
- Roll number
- Class
- Address
For store Student name and Address we need character data type, for Roll number and class we need integer data type.
If we are using Array then we need to defined separate variable.
Example
char student_name[10], address[20];
int roll_no[5], class[5];
If we use Structure then we use single variable for all data.
Syntax
struct stu
{
char student_name[10];
char address[20];
int roll_no[5];
int class[5];
};
Note: Minimum size of Structure is one byte and Maximum size of Structure is sum of all members variable size.
Note: Empty Structure is not possible in C Language.
Defining a Structure
Syntax
struct tagname
{
Datatype1 member1;
Datatype2 member2;
Datatype3 member3;
...........
};
At end of the structure creation (;) must be required because it indicates that an entity is constructed.
Example
struct emp
{
int id;
char name[36];
int sal;
};
sizeof(struct emp) // --> 40 byte (2byte+36byte+2byte)
Syntax to create structure variable
struct tagname variable;
Difference Between Array and Structure
| Array | Structure |
|---|
| 1 | Array is collection of homogeneous data. | Structure is the collection of heterogeneous data. |
| 2 | Array data are access using index. | Structure elements are access using . operator. |
| 3 | Array allocates static memory. | Structures allocate dynamic memory. |
| 4 | Array element access takes less time than structures. | Structure elements takes more time than Array. |
Example of Structure in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
struct emp
{
int id;
char name[36];
float sal;
};
void main()
{
struct emp e;
clrscr();
printf("Enter employee Id, Name, Salary: ");
scanf("%d",&e.id);
scanf("%s",&e.name);
scanf("%f",&e.sal);
printf("Id: %d",e.id);
printf("\nName: %s",e.name);
printf("\nSalary: %f",e.sal);
getch();
}
Output
Output: Enter employee Id, Name, Salary: 5 Spidy 45000 Id : 05 Name: Spidy Salary: 45000.00
Syntax to access structure members
By using following operators we can access structure members.
Syntax
. struct to member
--> pointer to member
When the variable is normal type then go for struct to member operator.
When the variable is pointer type then go for pointer to member operator.
Difference Between Structure and Pointer in C
Structure in C refer to a collection of various data types for example you create a structure named "Student" which contains his name , roll no, DOB etc. Name is string, Roll no is int.
While pointer refer to address in C
& symbol are used to point some particular place in C memory.
Union
A union is quite similar to the structures in C. It also store different data types in the same memory location. It is also a user defined data type same like structure.
union and structure are almost same
| Structure | Union |
|---|
struct student
{
int roll;
char name[10];
float marks;
}u;
| union student
{
int roll;
char name[10];
float marks;
}u;
|
Defining a union
Union can be defined in same manner as structures, for defining union use union keyword where as for defining structure use struct keyword.
Syntax
union tagname
{
datatype member1;
datatype member2;
.......
.......
};
Example of Union
union emp
{
int ID;
char name[10];
double salary;
}u;
Accessing members of an union
The member of unions can be accessed in similar manner as Structure with union reference. Suppose, we you want to access name variable in above example, it can be accessed as u.name.
Advantage of union over structure
It occupies less memory because it occupies the memory of largest member only.
Disadvantage of union over structure
It can store data in one member only.
Difference between Structure and Union
| Structure | Union |
|---|
| 1 | For defining structure use struct keyword. | For defining union we use union keyword |
| 2 | Structure occupies more memory space than union. | Union occupies less memory space than Structure. |
| 3 | In Structure we can access all members of structure at a time. | In union we can access only one member of union at a time. |
| 4 | Structure allocates separate storage space for its every members. | Union allocates one common storage space for its all members. Union find which member need more memory than other member, then it allocate that much space |
Memory Allocation in Structure and Union
Structure allocates separate storage space for its every members. Union allocates one common storage space for its all members. Union find which member need more memory than other member, then it allocate that much space
In case of Structure
Syntax
struct emp
{
int ID;
char name[10];
double salary;
};
Example
For above structure, memory allocation like below.
int ID -- 2B
char name[10] -- 10B
double salary -- 8B
Total memory allocation = 2+6+8 = 16 Bytes
In case of Union
Syntax
union emp
{
int ID;
char name[10];
double salary;
};
For above union, only 8 bytes of memory will be allocated because double data type will occupy maximum space of memory over other data types.
Total memory allocation = 8 Bytes
When use Structure and Union
When need to manipulate the data for all member variables then use structure. When need to manipulate only one member then use union.
Note:
- All the properties of the structure are same for union, except initialization process.
- In case of structure initialize all data members at a time because memory location are different but in case of union only one member need to be initialize.
- In case of union if we initializing multiple member then compiler will gives an error.
Example of Union in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
union emp
{
int ID;
char name[10];
double salary;
}u; // reference of union
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf("Enter emp Id: ");
scanf("%d",&u.ID);
printf("Enter emp Name: ");
scanf("%s",&u.name);
printf("Enter emp Salary: ");
scanf("%f",&u.salary);
printf("Emp ID: %d",u.ID);
printf("Emp Name: %s",u.name);
printf("Emp Salary: %f",u.salary);
getch();
}
Output
Output:
Emp ID: 100
Emp Name: Porter
Emp Salary: 20000